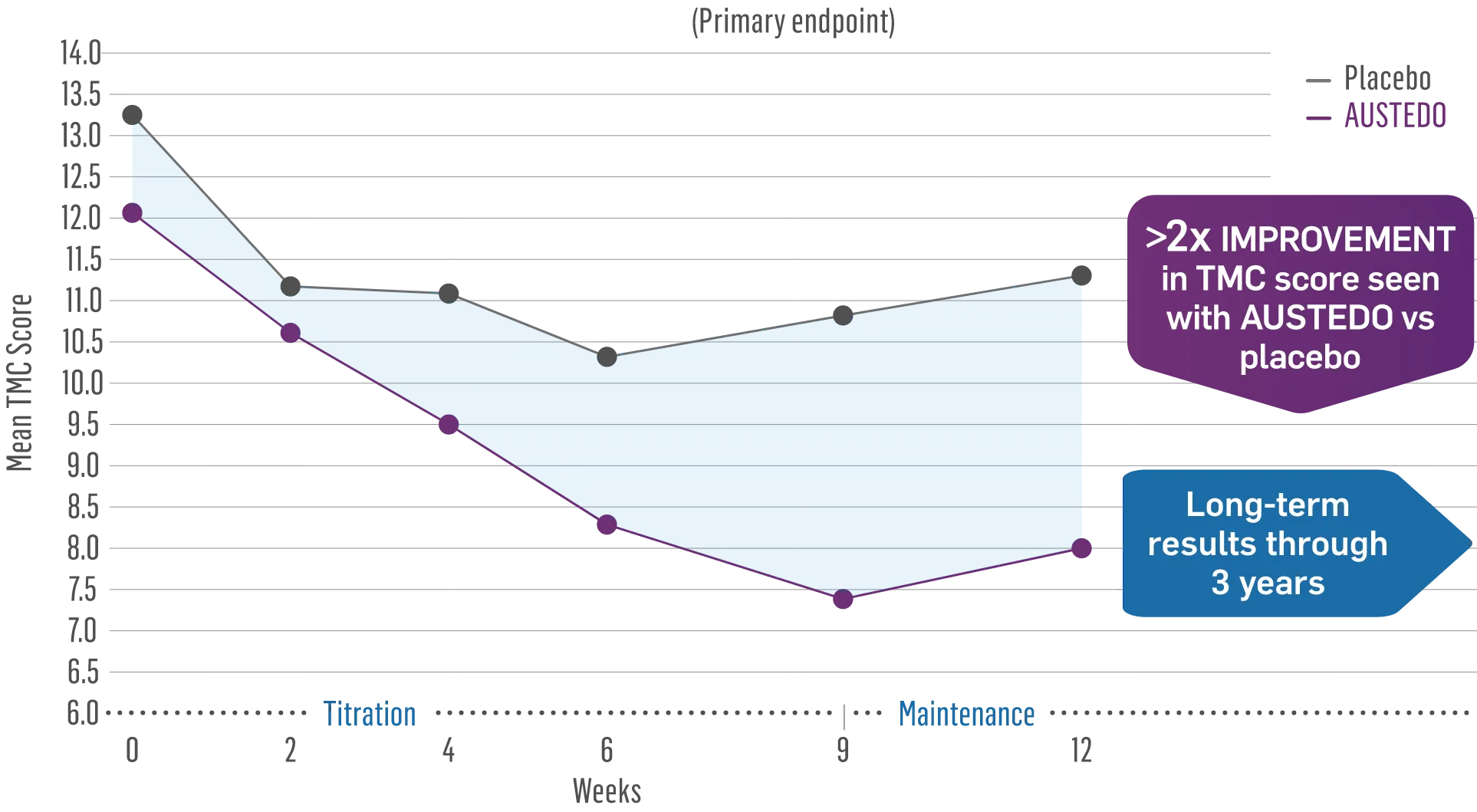
AUSTEDO provides significant chorea control1
AUSTEDO reduced total maximal chorea (TMC) score by 4.4 points from baseline (P<0.0001)1*
FIRST-HD Primary Endpoint: Change in TMC Score From Baseline to Maintenance Therapy (N=90, ITT)1-3
~40% reduction in chorea severity
vs baseline at Week 12
~40 mg/day†
Patients in the pivotal and long-term studies received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.1,4
~90% of patients saw improvement in their movements
vs baseline2‡
- 33% of patients achieved a ≥6-point improvement
compared to 2% of patients treated with placebo
ITT, intent-to-treat.
*Versus maintenance therapy (average of Weeks 9 and 12).1
†Mean total dose.1
‡Patients saw a ≥1-point reduction in TMC score by Week 12.1
The TMC score quantifies choreic movements of the face, mouth, trunk, both arms, and both legs, resulting in an overall score for the 7 regions that is based on independent visual review.2
Sustained concentrations with a single daily pill1
- Bioequivalence established between single-pill and multiple-pill doses of once-daily AUSTEDO XR based on pharmacokinetic studies1,2
- Data support bioequivalence of single-pill and multiple-pill AUSTEDO XR across full dosing range1
Plasma Concentration Over 96 Hours: AUSTEDO XR 48 mg vs AUSTEDO XR 2×24 mg QD2§
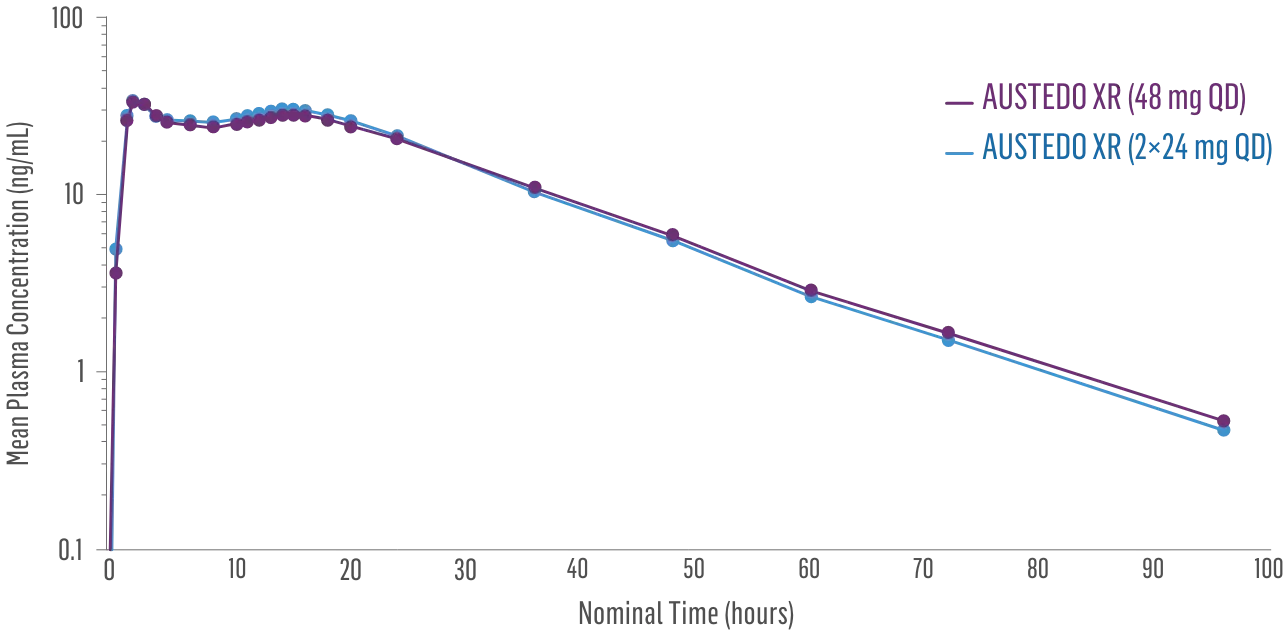
§Based on active alpha and beta metabolites.2
- Bioequivalence of once-daily AUSTEDO XR has been established in pharmacokinetic profile studies2||
- Peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) of AUSTEDO XR (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets are reached within approximately 3 hours1
Plasma Concentration at Steady State Over 24 Hours: AUSTEDO XR vs BID2¶
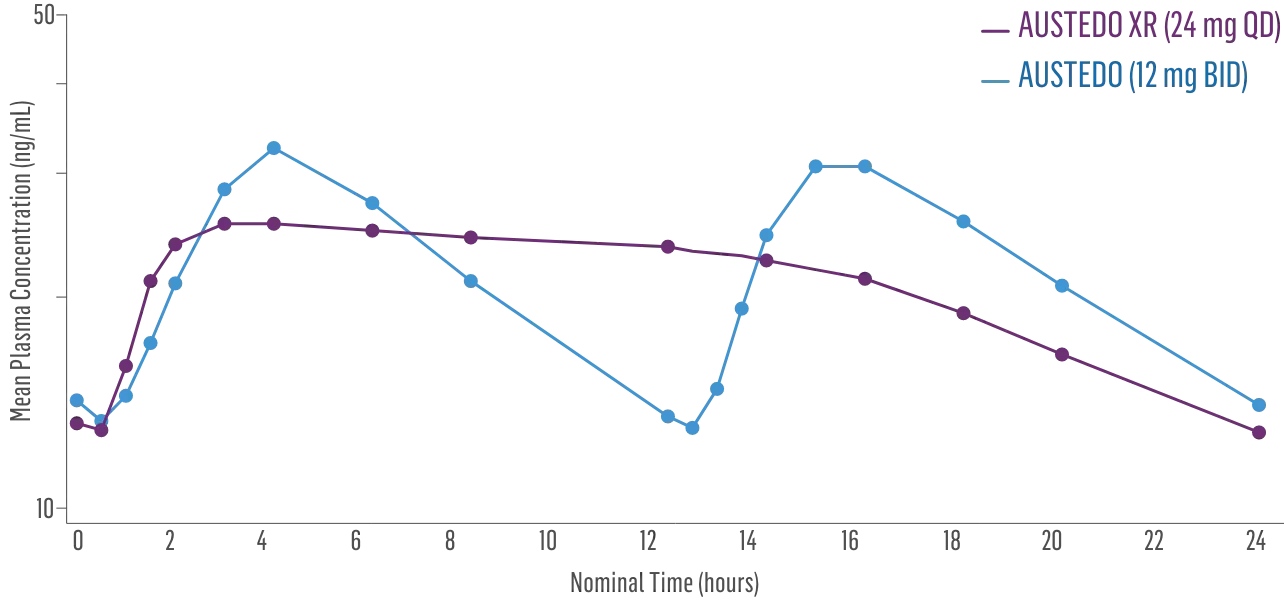
||Data support bioequivalence of XR and BID across the full dosing range of AUSTEDO.1
¶Based on active alpha and beta metabolites.2
AUSTEDO reduced total motor score (TMS), improving control of motor function2
FIRST-HD: LS Mean Change in TMS From Baseline to Maintenance Therapy (N=90, ITT)2
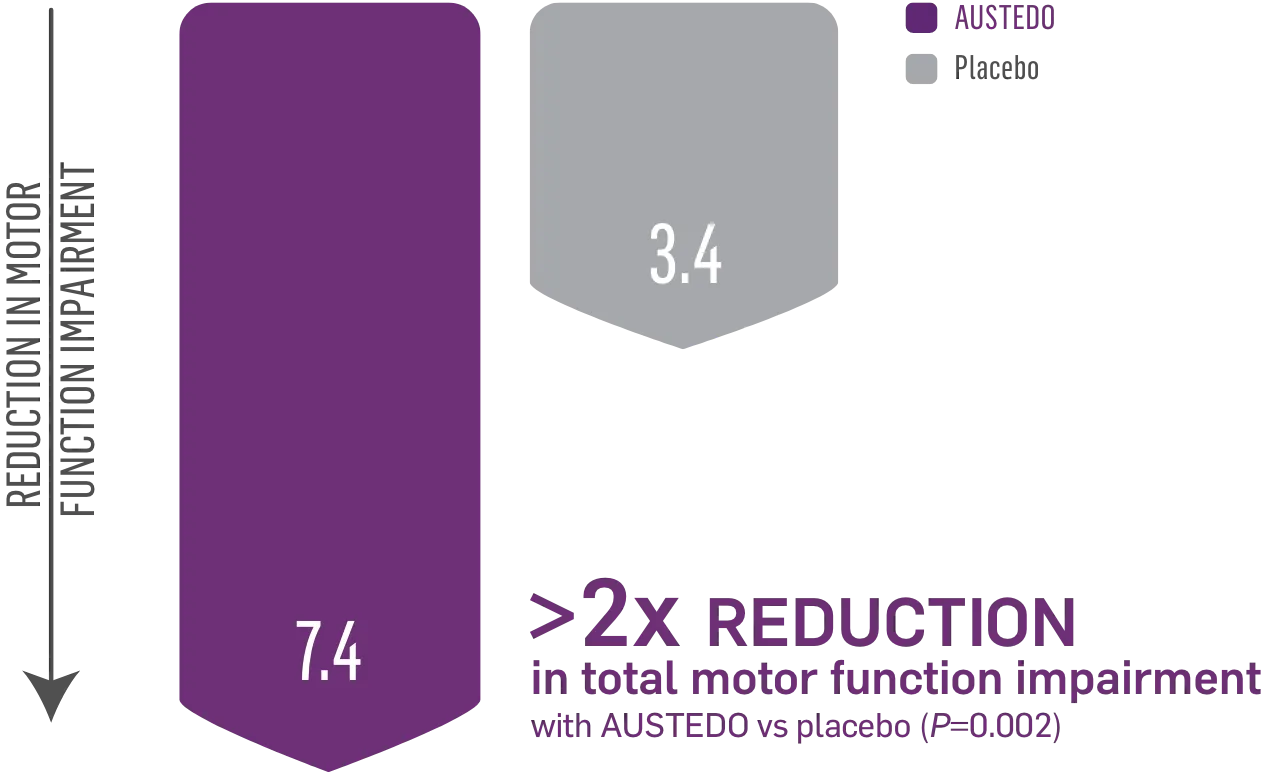
LS, least squares.
Patients in the pivotal study received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.1
TMS confirms the clinical relevance of the change in TMC. The TMS assesses all domains of motor dysfunction in HD, including chorea, dystonia, initiation of voluntary movement (dysarthria, tongue protrusion, finger tapping, hand pronation, and supination of hands), gait, and balance.2
Significant 4.3-point difference in SF-36 physical functioning score vs placebo (P=0.03)2,5
Patients taking placebo had a decline in physical functioning as measured by SF-36
The physical functioning portion of the SF-36 assesses patients’ reported ability to perform routine physical activities, such as:

Only VMAT2 inhibitor with patient-reported improvement in ability to perform activities of daily living2,5
FIRST-HD: SF-36 Physical Functioning Score (N=90, ITT)2
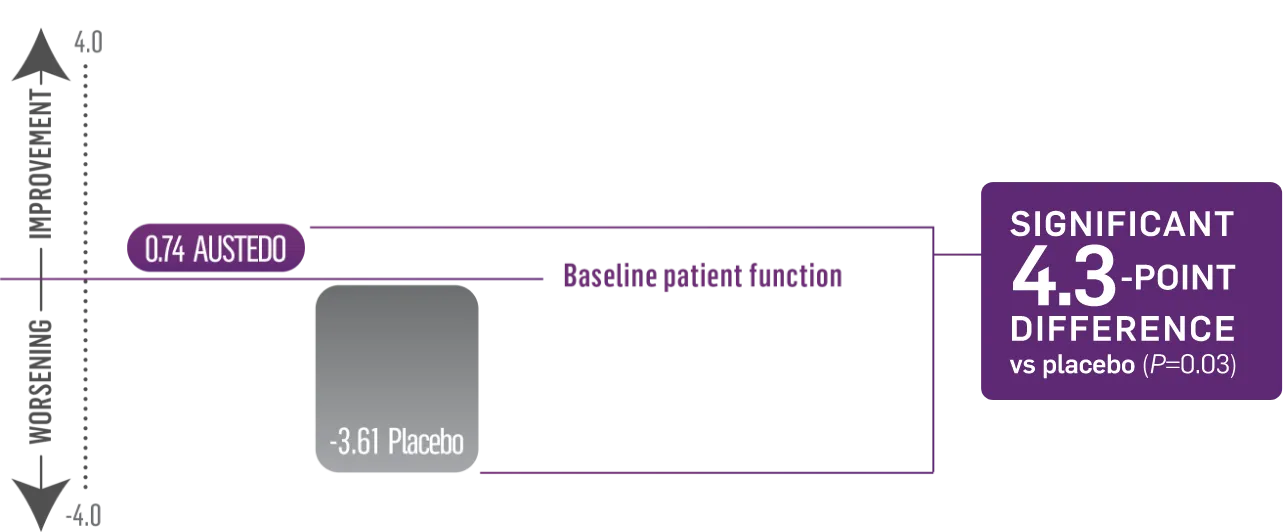
Patients in the FIRST-HD study received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.1
The impact of HD chorea on daily activities: Ray and Rhonda’s story
For more videos, visit the YouTube page.
Onscreen text:
HD chorea
THE IMPACT OF HD CHOREA ON DAILY ACTIVITIES
RAY & RHONDA’S STORY
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
This was an individual patient’s experience. Results may vary. Ray and Rhonda were compensated for their participation in this video.
Onscreen text:
HD, Huntington’s disease.
Rhonda:
As the movements progressed more and more, I was thinking about what equipment he would need for getting dressed or taking a shower. OR if he would need a wheelchair.
On-screen text:
99% of patients with HD chorea require assistance with self-care activities.
When Ray was diagnosed with HD in 2019, his chorea had already begun limiting his physical functioning.
Ray:
I first noticed my involuntary movements when we were working…and my hand would just shake. I was just thinking, what’s going on?
Rhonda:
I was noticing at night when we were sleeping…he would be kicking me or hitting…he was just flailing around, moving his arms and legs.
Onscreen text:
As Ray’s symptoms worsening, Ray and his wife, Rhonda, knew it was time to talk to his doctor.
Rhonda:
We spoke with the doctor about it, and we didn’t know if there was any options for dealing with the chorea or not.
But we did talk to her and let her know that this has been going on for quite some time, and just wondering if there was any help for that.
Onscreen text:
The physical functioning portion of the SF-36 questionnaire, a health-related quality of life scale, was used to assess the impact of Ray’s chorea on daily activities.
Bathing
Lifting/carrying groceries
Walking
Moderate to vigorous activities
Climbing stairs
Bending, kneeling, or stooping
SF-36, Short Form Health Survey.
Based on Ray’s symptoms and the impact his chorea had on his activities of daily living, he was prescribed AUSTEDO.
Onscreen Indication and Black Box Warning:
AUSTEDO XR® and AUSTEDO® are indicated in adults for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Please see additional Important Safety Information at the end of this video.
Onscreen text:
Patients taking AUSTEDO, like Ray, reported being better able to perform activities of daily living—with a significant 4.3-point difference in SF-36 physical functioning score in the pivotal trial.
Patients taking placebo had a decline in physical functioning as measured by SF-36
Rhonda:
He’s able to still do all the daily activities that one does during the day, all the ordinary things that sometimes the rest of us would take for granted.
Onscreen text:
More than 3 years later, Ray is still taking AUSTEDO at 48 mg/day. His chorea movements have remained minimal, and he’s better able to perform activities of daily living.
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
Once-daily AUSTEDO XR is available.
Bioequivalence of once-daily AUSTEDO XR has been established with AUSTEDO BID based on pharmacokinetic profile studies. When two formulations are shown to be bioequivalence, they are considered to be therapeutically equivalent.
Rhonda:
Starting early on AUSTEDO has made a big difference in what we’re able to do now.
It keeps his movements at bay, keeps us hiking and walking and traveling and doing things that I don’t believe we would be able to do had he not got it started.
We’re actually like living the way we’ve always wanted to live now. I can’t imagine life if he didn’t have it.
Onscreen text:
Learn more about how AUSTEDO could make a different for your patients’ physical functioning at AUSTEDOhcp.com
Onscreen ISI scroll:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are indicated in adults for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia and for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington's disease.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Contraindications: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients with Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are also contraindicated in: patients with hepatic impairment; patients taking reserpine or within 20 days of discontinuing reserpine; patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOI therapy; and patients taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine.
Clinical Worsening and Adverse Events in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause a worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity.Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in their patients by assessing the effect on chorea and possible adverse effects.
QTc Prolongation: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may prolong the QT interval, but the degree of QT prolongation is not clinically significant when AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is administered within the recommended dosage range. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias. Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex reported in association with drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission, has been observed in patients receiving tetrabenazine. The risk may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. The management of NMS should include immediate discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO; intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems.
Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of akathisia, agitation, and restlessness. The risk of akathisia may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops akathisia, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Parkinsonism: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause parkinsonism in patients with Huntington’s disease or tardive dyskinesia. Parkinsonism has also been observed with other VMAT2 inhibitors. The risk of parkinsonism may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops parkinsonism, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Sedation and Somnolence: Sedation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and know how the drug affects them. Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence.
Hyperprolactinemia: Tetrabenazine elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO.
Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues: Deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues and could accumulate in these tissues over time. Prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects.
Common Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (>8% and greater than placebo) in a controlled clinical study in patients with Huntington’s disease were somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (4% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, at AUSTEDOhcp.com.
Onscreen text:
This was an individual patient’s experience. Results may vary.
References: 1. Claassen DO, DeCourcy J, Mellor J, Johnston C, Iyer RG. Impact of chorea on self-care activity, employment, and health-care resource use in patients with Huntington’s disease. J Health Econ Outcomes Res. 2021;8(1):99-105. 2. Data on file. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc. 3. RAND Corporation. 36-Item Short Form Survey Instrument (SF-36). RAND Corporation. Accessed November 12, 2022. https://www.rand.org/health-care/surveys_tools/mos/36-item-short-form/survey-instrument.html
Treatment success recognized by both patients and physicians1#
FIRST-HD: Global Impression of Change at the End of Treatment for AUSTEDO Compared to Placebo (N=90, ITT)2,3
PATIENT GLOBAL IMPRESSION OF CHANGE (PGIC)
much improved
20%
51%
of Patients Observed
Treatment Success#
(P=0.002)
CLINICAL GLOBAL IMPRESSION OF CHANGE (CGIC)
much improved
13%
42%
of Physicians Observed
Treatment Success#
(P=0.002)
Patients in the FIRST-HD study received the AUSTEDO BID formulation.1
#Treatment success was defined as “much improved” or “very much improved” at Week 12.2
- The PGIC and the CGIC are patient- and provider-centered endpoints2,3
- Patients and providers are asked to describe HD symptoms now compared to immediately before the start of treatment2,3
- A randomized, 12-week, placebo-controlled study of the use of AUSTEDO in patients with chorea associated with HD1,3
- Patients were randomized to receive AUSTEDO (n=45) or placebo (n=45)1,3
- The mean age of patients taking AUSTEDO was 55.4 years (vs 52.1 years with placebo)3
- 62% of patients on AUSTEDO were concomitantly taking antidepressants (vs 53% with placebo)2
- The primary efficacy endpoint was the treatment effect of AUSTEDO vs placebo, as measured by the TMC score, an item of the Unified Huntington’s Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS), from baseline to maintenance1
- On this scale, chorea is rated from 0 to 4 (with 0 representing no chorea) for 7 different parts of the body. The total score ranges from 0 to 28
- The combined group mean TMC score at baseline was 12.73
- An open-label, single-arm, 2-cohort, 3-year extension study of the use of AUSTEDO in patients with HD chorea
- The Rollover cohort had successfully completed FIRST-HD and underwent a
1-week washout prior to initiating 6 mg of AUSTEDO daily - The Switch cohort comprised patients with HD chorea who had been on a stable dose of tetrabenazine and were converted overnight to a dose of AUSTEDO predicted to provide comparable systemic exposure
- A total of 119 patients with HD chorea were enrolled (Rollover cohort, n=82; Switch cohort, n=37)
- In both cohorts, dosage was titrated by 6 mg/day per week
- Endpoints were changes in the UHDRS TMS and TMC scores from baseline to Week 8, as well as those from Week 8 to Week 145 (or end of treatment), and exposure-adjusted incidence rates of adverse events
Watch: Dr. Rajeev Kumar discuss SF-36 results and impact on activities of daily living
For more videos, visit the YouTube page.
Voiceover/Onscreen text:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO® XR (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO® (deutetrabenazine) tablets are indicated in adults for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease and for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease:
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Please see additional Important Safety Information at the end of this video.
Rajeev Kumar:
Hello. I’m Dr. Rajeev Kumar, Medical Director of the Rocky Mountain Movement Disorders Center and Huntington’s Disease Society of America Center of Excellence in Colorado. For over 20 years, I have been working with patients to treat their chorea symptoms.
I was involved in the evaluation of AUSTEDO in the pivotal trial for treatment of chorea associated with HD. I chose to be involved because the success of this trial could lead to a treatment for my patients with chorea.
I had a conversation with a colleague the other day about our patients with HD chorea. AUSTEDO is an appropriate choice to treat those symptoms, and I thought it’d be insightful to share some of our discussion with you.
My colleague said he was concerned about the impact chorea symptoms were having on his patients and their caregivers. He was particularly concerned about patients who were not aware of their symptoms and had become increasingly reliant on their caregivers. Even when patients are not aware of their symptoms, it is still important to treat them because of the impact chorea can have on their ability to function and their need for daily assistance.
The efficacy and safety of AUSTEDO were demonstrated in a randomized, 12-week placebo-controlled study in patients with chorea. The primary endpoint was total maximal chorea, or TMC, score. AUSTEDO reduced TMC score by 4.4 points from baseline, more than twice the improvement in the TMC score from placebo. The reduction in chorea was demonstrated in the face, mouth, trunk, and legs.
In my experience, after patients begin treatment, they often acknowledge improvements in areas of self-care and activities of daily living. My colleague and I talked about how we have observed improvement in our patients first-hand—particularly in areas of daily living, including walking, bathing, dressing, lifting, carrying groceries, moderate to vigorous activities, or climbing stairs.
Both patients and clinicians reported treatment success as measured by the Patient Global Impression of Change, or PGIC, and Clinical Global Impression of Change, or CGIC. Treatment is considered successful when symptoms are rated as “much improved” or “very much improved.” On the PGIC, the patient success rate with AUSTEDO was 51 percent, compared with 20 percent for placebo.
The physical function portion of the Short-Form 36 Health Survey, known as the SF-36, supported these findings as well. In the clinical trial for AUSTEDO, there was a statistically significant reduction in disability and improvement in physical functioning compared with placebo at 12 weeks.
While we were talking about study results, I mentioned that I tell my patients the most common side effects can include drowsiness, dry mouth, diarrhea, and fatigue. And I encourage them to share with me any symptoms they find bothersome.
Disclaimer at bottom of screen:
Patients who participated in the clinical trials discussed in this testimonial received the BID formulation of AUSTEDO.
Rajeev Kumar:
In my practice, I have been pleased with the experience my patients with HD chorea have had with AUSTEDO, particularly with their improvements in areas of daily living, physical functioning, and reduced disability. In addition to managing symptoms, I am always looking for opportunities to offer my patients a choice. With the availability of AUSTEDO XR, my patients have the option to take their treatment once daily.
Voiceover/Onscreen text:
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
AUSTEDO® XR (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO® (deutetrabenazine) are indicated in adults for the treatment of chorea associated with Huntington’s disease and for the treatment of tardive dyskinesia.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
Depression and Suicidality in Patients with Huntington’s Disease:
AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO can increase the risk of depression and suicidal thoughts and behavior (suicidality) in patients with Huntington’s disease. Balance the risks of depression and suicidality with the clinical need for treatment of chorea. Closely monitor patients for the emergence or worsening of depression, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Inform patients, their caregivers, and families of the risk of depression and suicidality and instruct them to report behaviors of concern promptly to the treating physician. Exercise caution when treating patients with a history of depression or prior suicide attempts or ideation. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients who are suicidal, and in patients with untreated or inadequately treated depression.
Contraindications: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are contraindicated in patients with Huntington’s disease who are suicidal, or have untreated or inadequately treated depression. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO are also contraindicated in: patients with hepatic impairment; patients taking reserpine or within 20 days of discontinuing reserpine; patients taking monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), or within 14 days of discontinuing MAOI therapy; and patients taking tetrabenazine or valbenazine.
Clinical Worsening and Adverse Events in Patients with Huntington’s Disease: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause a worsening in mood, cognition, rigidity, and functional capacity. Prescribers should periodically re-evaluate the need for AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO in their patients by assessing the effect on chorea and possible adverse effects.
QTc Prolongation: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may prolong the QT interval, but the degree of QT prolongation is not clinically significant when AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO is administered within the recommended dosage range. AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO should be avoided in patients with congenital long QT syndrome and in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias.
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS), a potentially fatal symptom complex reported in association with drugs that reduce dopaminergic transmission, has been observed in patients receiving tetrabenazine. The risk may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics, The management of NMS should include immediate discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO; intensive symptomatic treatment and medical monitoring; and treatment of any concomitant serious medical problems.
Akathisia, Agitation, and Restlessness: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may increase the risk of akathisia, agitation, and restlessness. The risk of akathisia may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops akathisia, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Parkinsonism: AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO may cause parkinsonism in patients with Huntington’s disease or tardive dyskinesia. Parkinsonism has also been observed with other VMAT2 inhibitors. The risk of parkinsonism may be increased by concomitant use of dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics. If a patient develops parkinsonism, the AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO dose should be reduced; some patients may require discontinuation of therapy.
Sedation and Somnolence: Sedation is a common dose-limiting adverse reaction of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Patients should not perform activities requiring mental alertness, such as operating a motor vehicle or hazardous machinery, until they are on a maintenance dose of AUSTEDO XR or AUSTEDO and know how the drug affects them. Concomitant use of alcohol or other sedating drugs may have additive effects and worsen sedation and somnolence.
Hyperprolactinemia: Tetrabenazine elevates serum prolactin concentrations in humans. If there is a clinical suspicion of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia, appropriate laboratory testing should be done and consideration should be given to discontinuation of AUSTEDO XR and AUSTEDO. Binding to Melanin-Containing Tissues: Deutetrabenazine or its metabolites bind to melanin-containing tissues and could accumulate in these tissues over time. Prescribers should be aware of the possibility of long-term ophthalmologic effects.
Common Adverse Reactions: The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (>8% and greater than placebo) in a controlled clinical study in patients with Huntington’s disease were somnolence, diarrhea, dry mouth, and fatigue. The most common adverse reactions for AUSTEDO (4% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical studies in patients with tardive dyskinesia were nasopharyngitis and insomnia. Adverse reactions with AUSTEDO XR extended-release tablets are expected to be similar to AUSTEDO tablets.
Please see full Prescribing Information, including Boxed Warning, at AUSTEDOhcp.com.
HD, Huntington’s disease; SF-36, Short Form (36) Health Survey.
REFERENCES: 1. AUSTEDO XR® (deutetrabenazine) extended-release tablets and AUSTEDO® current Prescribing Information. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc. 2. Data on file. Parsippany, NJ: Teva Neuroscience, Inc. 3. Frank S, Testa CM, Stamler D, et al; Huntington Study Group. Effect of deutetrabenazine on chorea among patients with Huntington disease: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2016;316(1):40-50. 4. Frank S, Testa C, Edmondson MC, et al. The safety of deutetrabenazine for chorea in Huntington disease: an open-label extension study. CNS Drugs. 2022;36(11):1207-1216. 5. RAND Corporation. 36-Item Short Form Survey Instrument (SF-36). RAND Corporation. Accessed April 4, 2025. https://www.rand.org/health-care/surveys_tools/mos/36-item-short-form/survey-instrument.html
